Advanced muscle-building and endurance formulas to help you reach the peak of your performance and recovery.
Why Creatine?
Before we get into a little science and biology, it’s worth noting that Creatine has been the subject of over 500 published studies and 100 published human studies, making it one of the most researched dietary supplements over the past four decades. It’s effectiveness and safety for healthy adults is widely recognised, however it is advised to follow a planned daily-intake strategy, consistently.
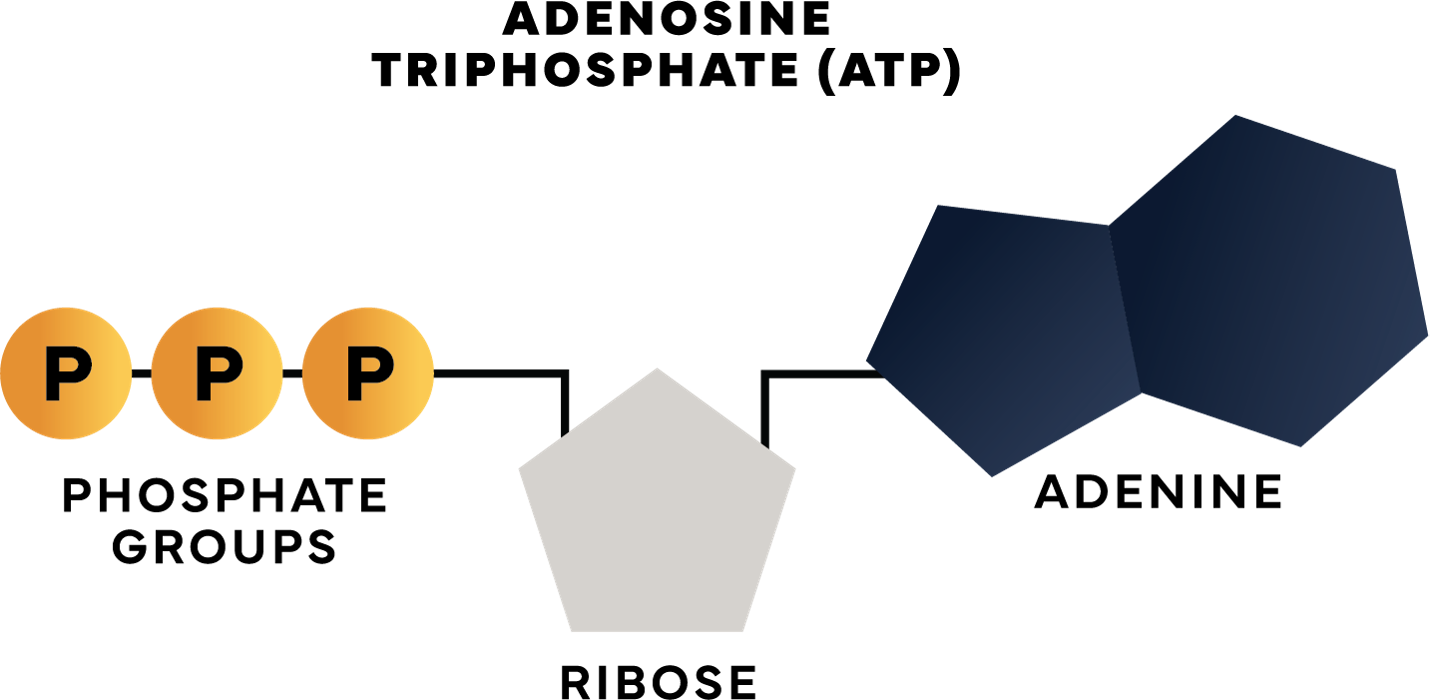
Now let’s dive into the production of energy in the body. Every cell needs energy to function and muscle cells need it to contract. This energy is in the form of a molecule called ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate).
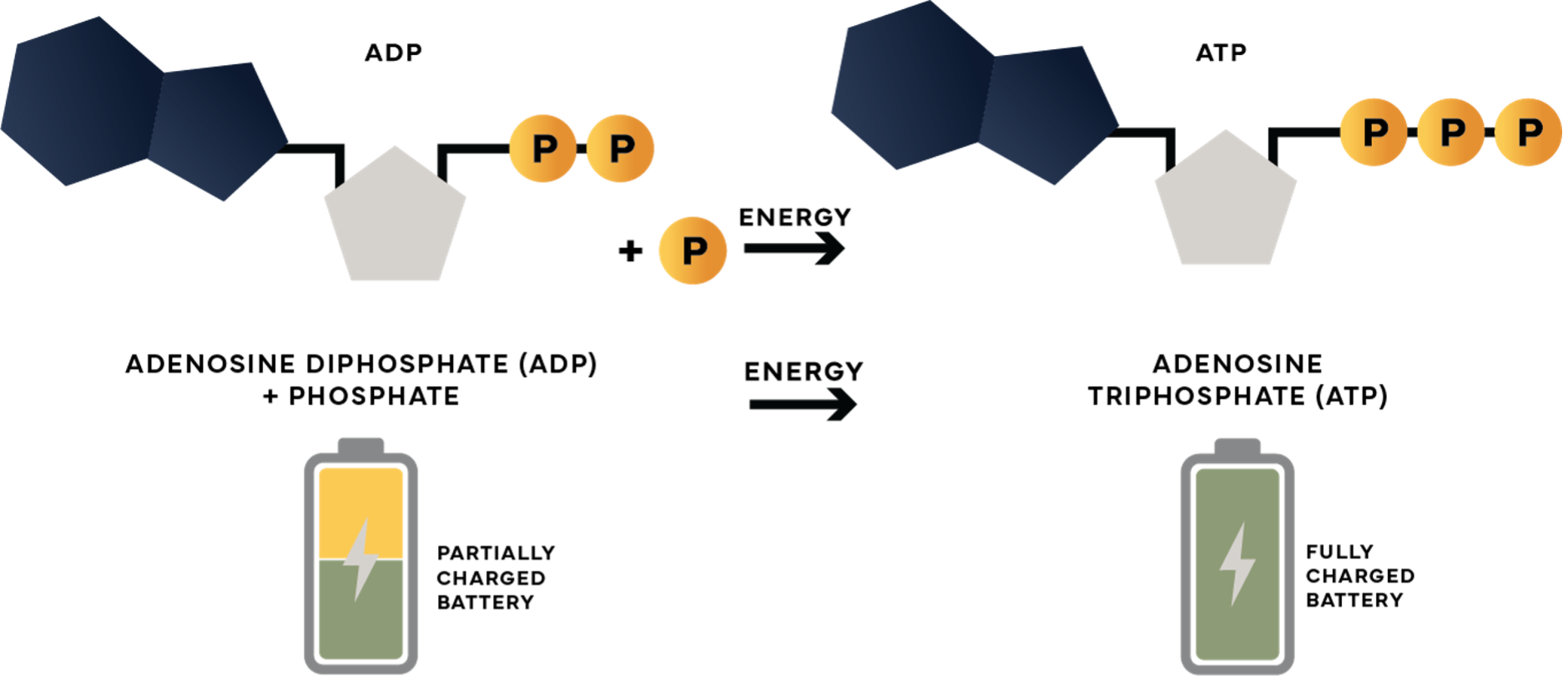
Energy is produced when one of the three phosphate groups is removed from the ATP molecule. Once the phosphate group is removed, only two remain. The molecule with the remaining groups is now called ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate).
The interesting thing about ADP is that it can be ‘recycled’ to produce energy again. If a third phosphate group is reintroduced to the two remaining groups, then ATP is generated again and becomes a renewed source of energy.
This brings us back to Creatine. When we consume Creatine, the body converts Creatine (as a supplement, Creatine Monohydrate is the most widely researched) to Creatine Phosphate. Creatine Phosphate donates its phosphate group to ADP, thus making ATP.